As an outcome of the successful campaign led by citizens and the civil society, the Turkish Ministry of Environment and Urbanization announced on the first days of 2020 that five coal-fired power plants totally and one coal-fired power plant partially stopped operation. Right to Clean Air Platform, as an important actor of the campaign, emphasized that 2020 can be a milestone for accessing clean air in Turkey and requested monitoring of the PM 2.5 pollutant in all cities of Turkey and the adoption of national limits.
Call for legislative arrangements in Turkey
Platform mentioned that Turkey still lacks official limit values for PM 2.5 which is one of the most harmful air pollution-related pollutants for human health. Unlike other pollutants, PM 2.5 can easily enter the blood circulatory system and access the deeper parts of the respiratory system. In 2019, PM 2.5 is measured at only 81 monitoring stations out of 339 installed by the Turkish Ministry of Environment and Urbanisation. However, there have been no measures taken because unlike EU member countries, Turkey still does not have relevant legislation that sets national limits for PM 2.5 pollution.
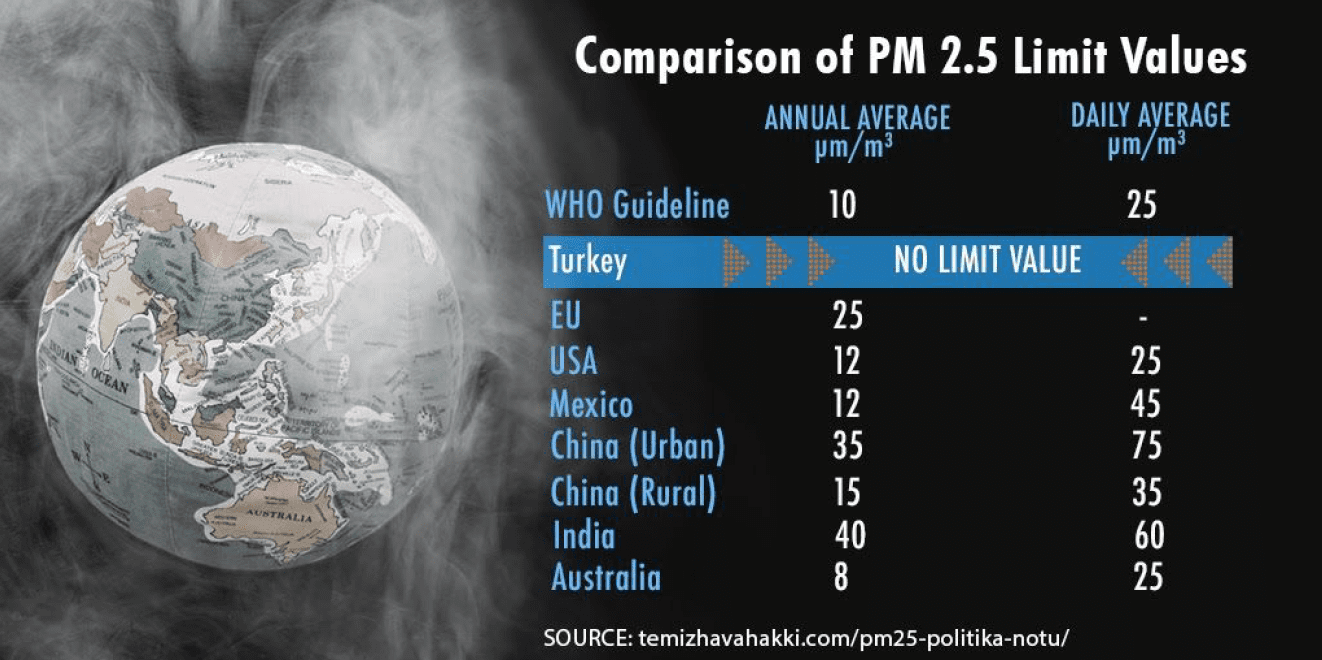
China has limits for PM 2.5 unlike Turkey
Right to Clean Air Platform / Doctors for Environment representative Prof. Ali Osman Karababa provided a comparison about the air quality limits in different countries: “Several countries such as Australia, Canada, Japan, and the USA adopted national limits that are in line with the guideline values proposed by the World Health Organisation (WHO). Even in China, where coal production has the lion’s share in energy policies, there are regulations that set different PM 2.5 limits for urban and rural areas. However, Turkey lacks any regulation in order to limit or prevent PM 2.5 pollution and does not have decent data about the PM 2.5 levels in all cities. It is indispensable that national limits for PM 2.5 are determined in consideration of the WHO
guideline values and European Union limits in Turkey too.”
Right to Clean Air Platform / Turkish Medical Association representative Assoc. Prof. Dr. Gamze Varol stated that “ It is a correct decision to stop 6 coal-fired power plants that do not comply with the Environmental Law were sealed by the government officials. However, it is important to remember that, even if those coal plants are retrofitted and filters are installed; those plants will continue to cause air pollution and climate change as a result of their emissions. The main aim must be to improve the air quality in Turkey in such a way to have air pollution below WHO guideline values in line with the ‘right to live in a healthy environment’ in our constitution and international statements. In order to reach that target, we need permanent solutions that are in line with scientific principles and the needs of society. It can only be reached if the fossil fuels are abandoned and policies that will foster investments in energy efficiency and renewable energy resources are accelerated with a just planning that will compensate for the inequalities created in the past.’
Contacts:
- Buket Atlı, Coordinator of Right to Clean Air Platform-Turkey: [email protected]
- Funda Gacal, HEAL-Health and Environment Alliance, Consultant for Turkey: [email protected]
- Website: https://www.temizhavahakki.com/english
Notes for Editor:
What is PM2.5?
Particulate matter (PM) is the term for a pollutant that consists of a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Particulate matter is measured by micrometers (μg/m3) and named by its sizes such as PM 10 , PM 2.5 , and PM 0.1 . PM 2.5 is 30 times smaller than the average human hair and it can disperse for thousands of kilometers beyond country borders and
continents, thus it is an important indicator for the protection of public health.
Every year 8 million people in the world die due to their exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution. Ambient air pollution is responsible for 27.5% of deaths due to lower respiratory and 26.8% of deaths due to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
PM 2.5 is particularly important to protect public health because
- PM 2.5 causes more health risks PM 10 by reaching the deepest parts of the lungs and directly enter the blood circulatory system .
- PM 2.5 is the most common index used worldwide for the calculation of the burden and mortality due to air pollution-related diseases.
- The main source of PM 2.5 and smaller particulate matter (such as PM 0.1 ) is related to human activities such as heating, transportation, industry and electricity generation.
Right to Clean Air Platform Calls Ministry of Environment and Urbanisation to Action:
By the end of 2020, PM 2.5 pollution should be monitored in all stations in Turkey,
In the first quarter of 2020, Turkey’s national limit values for PM 2.5 should be determined,
PM 2.5 limit values to be determined should be in line with the WHO guidelines and European Union limit values which is also expected to be lowered in the coming years,
Health Impact Assessment (HIA) should be a part of the permitting processes for coal-fired power and large combustion plants,
Current legislation and air pollution dispersion model that is in use for the large combustion plants should be updated. The updated model should be able to calculate long-range contamination, cumulative effect and the effect of secondary pollutants.
About Right to Clean Air Platform-Turkey
Right to Clean Air Platform-Turkey, consists of 16 professional organizations and NGOs, working on air pollution and health impacts in Turkey since 2015. The aim of the Platform is to advocate for the right to live in an environment with clean air and to protect the public health from air pollution, especially resulting from the existing and planned coal-fired power plants in Turkey.
Platform Constituents are;
CAN Europe • General Practitioner Association of Turkey • Greenpeace Mediterranean • Green Peace Law Association • Green Thought Association • HEAL – Health and Environment Alliance • Physicians for Environment Association • Turkish Medical Association (TTB) • Turkish Neurological Society • Turkish Respiratory Society (TÜSAD) • Turkish Society of Occupational Health Specialists (İMUD) • Turkish Society of Public Health Specialists (HASUDER) • TEMA Foundation • Yuva Association • WWF-Turkey • 350.org